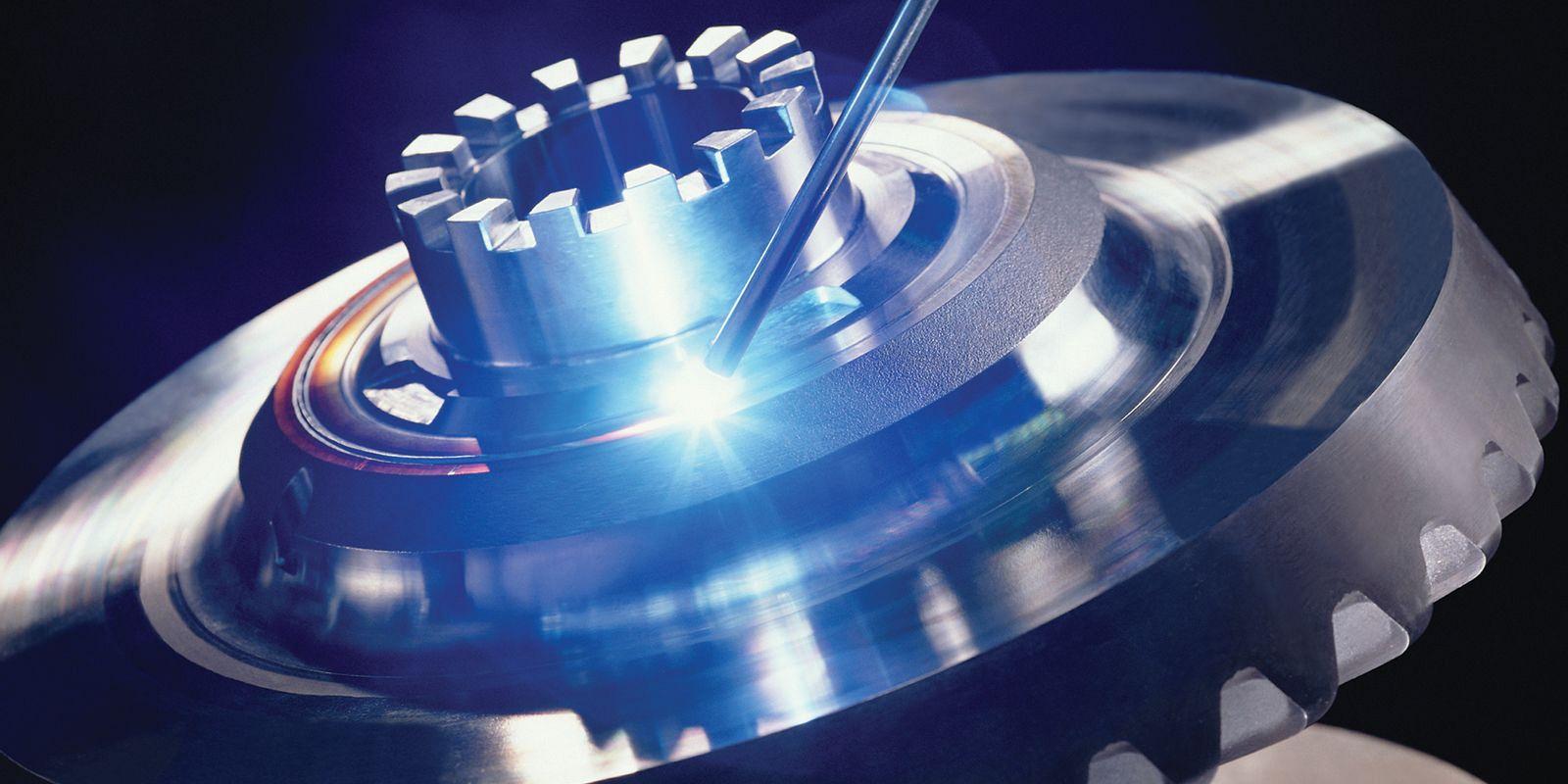
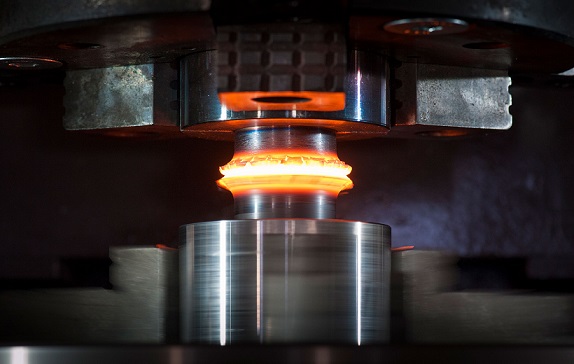
Brazing is a thermal joining process that uses a melted filler material to connect metal components. The filler material typically has a lower melting point than the components being joined, and it is used to fill the gap between the two components. Brazing is often used in applications where a strong, durable joint is required, such as in the aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries.
One of the main advantages of brazing is its relatively low heat input, which can help prevent distortion and damage to the components being joined. This makes it a useful process for joining dissimilar metals and for joining components that are sensitive to high heat. Brazing can also produce joints of considerable strength and durability, making it a popular choice for applications where reliability and longevity are important.
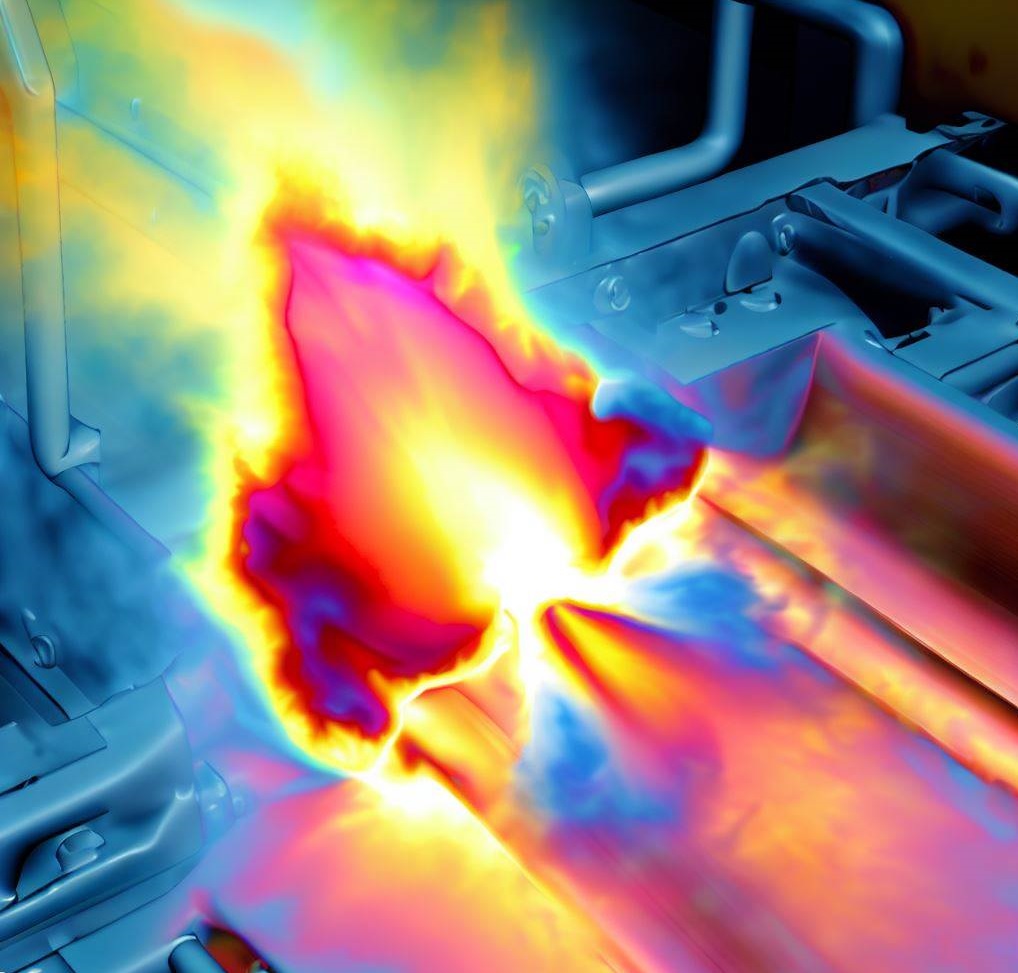
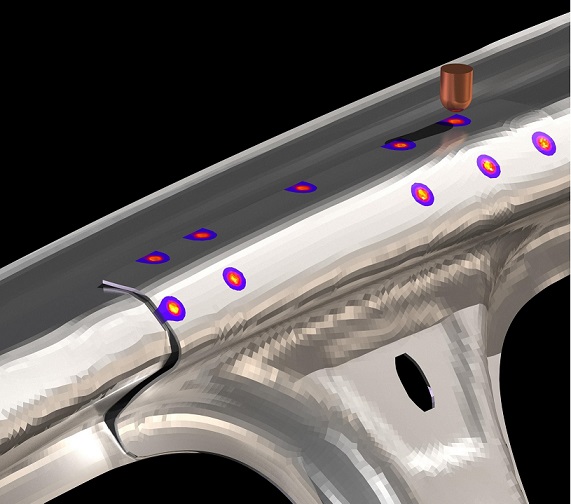
Simulation Dynamics engineers use innovative CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) and virtual prototyping techniques to simulate the brazing process. These techniques allow them to analyze the behavior of the joint and predict its performance under various conditions. Non-linear structural codes such as LS-DYNA, Ansys, Comsol, Simufact Welding, and ABAQUS are commonly used to simulate the brazing process and optimize the design of the joint.